Largest compact area of reed: world record set by The Danube Delta
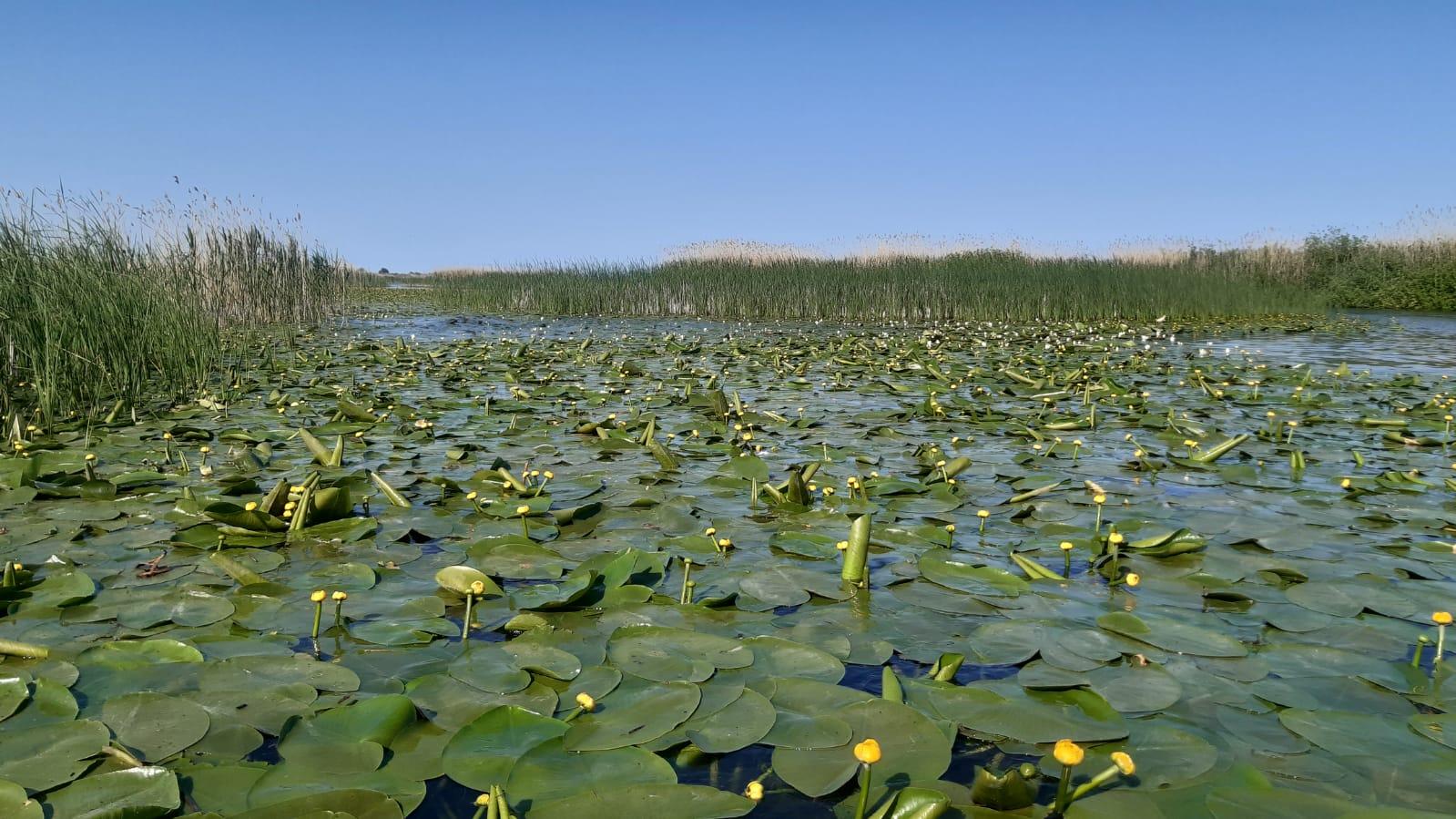

Vegetation of this ecosystem consists of the common reed (Phragmites communis) and, on near river banks, mace reed/cattail (Typha latifolia, Typha angustifolia), sedge (Carex dioica, Carex stricta), Dutch rush (Scirpus radicans, Schoenoplectus lacustris), and brook mint (Mentha aquatica), etc.
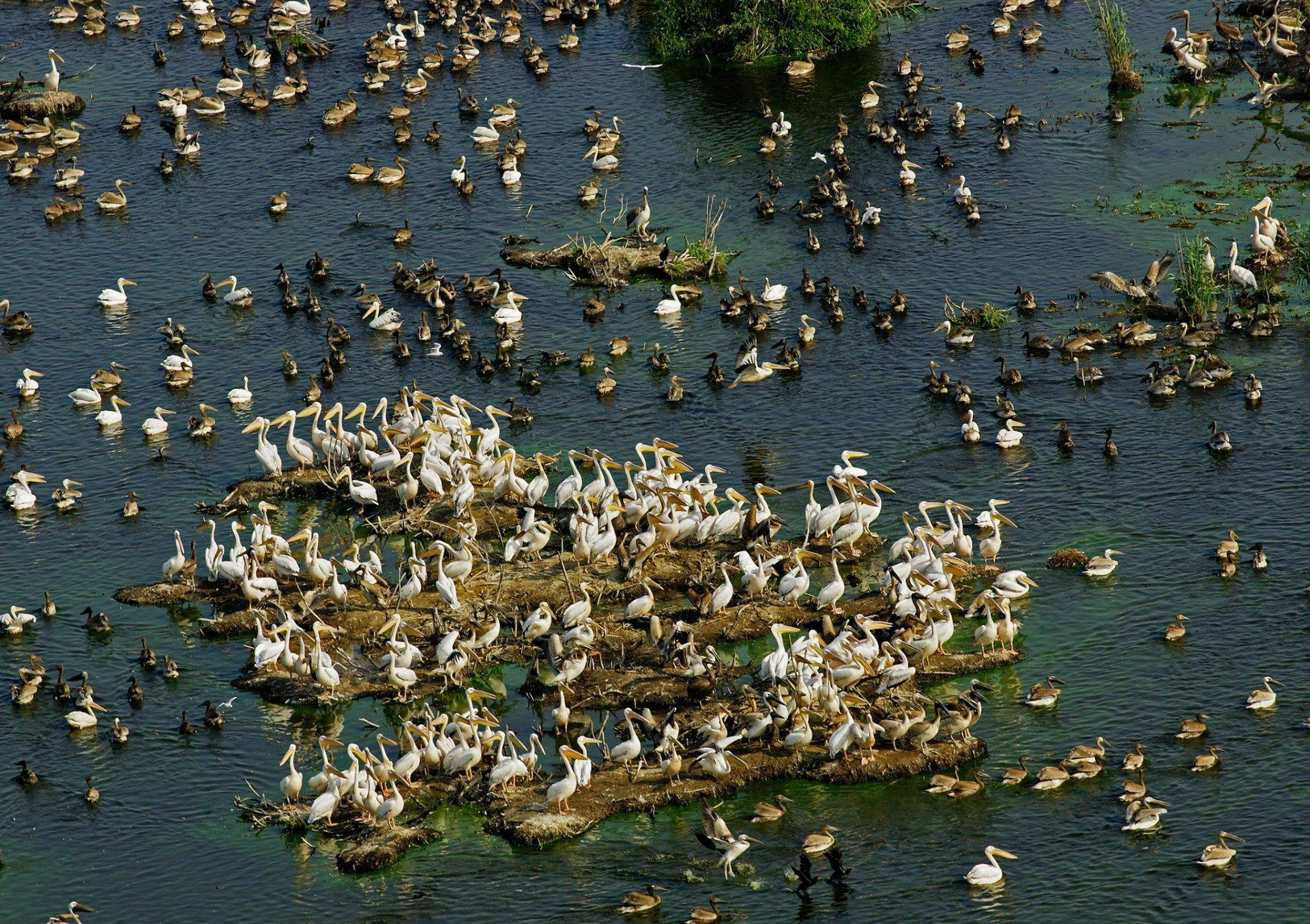
Situated on major migratory routes, and providing adequate conditions for nesting and hatching, the Danube Delta is a magnet for birds from six major ecoregions of the world, including the Mongolian, Arctic and Siberian. There are over 320 species of birds found in the delta during summer, of which 166 are hatching species and 159 are migratory. Over one million individual birds (swans, wild ducks, coots, etc.) winter here.
Reed plants and floating reed islands (called plaur in Romania) are the most common and well known components of the Danube Delta. Vegetation of this ecosystem consists of the common reed (Phragmites communis) and, on near river banks, mace reed/cattail (Typha latifolia, Typha angustifolia), sedge (Carex dioica, Carex stricta), Dutch rush (Scirpus radicans, Schoenoplectus lacustris), and brook mint (Mentha aquatica), etc. T
hey provide ideal spawning and nesting grounds. The plaur are a mixture of reed roots, grass and soil, usually floating or anchored to the riverbed. As a rule, the reed surrounds the lakes and ponds, and slowly invades the water surface.
Reed was intensively harvested during the Communist era. The regime had plans to transform the delta into a large agro-industrial zone. Although the first modern agricultural exploitation dates from 1939 (Ostrovul Tãtaru), only after 1960 were large areas drained and converted, to the detriment of the wetlands.
In 1991 agricultural land in the delta surpassed 100,000 hectares, and more than a third of its surface has been affected by crop cultivation, forest plantation, or fish farming. As a result of these changes, along with the increasing pollution and eutrophication of the waters of the Danube, and decades of exploitation and poor fishing regulations, the fish population has been visibly reduced.
Photos: Daniel Petrescu / Rezervația Biosferei Delta Dunării